- Dibutyl sebacate
-
Dibutyl sebacate[1] 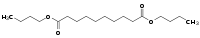 Other namesdibutyl sebacate
Other namesdibutyl sebacateIdentifiers CAS number 109-43-3 
ChemSpider 7697 
UNII 4W5IH7FLNY 
Properties Molecular formula C18H34O4 Molar mass 314.46 g mol−1 Appearance colorless liquid Density 0.9405 g/cm3 at 15°C Melting point -10°C
Boiling point 344.5°C
Solubility in water 0.04 g/L Solubility soluble in diethyl ether, carbon tetrachloride Structure Dipole moment 2.48 D Thermochemistry Specific heat capacity, C 1.968 J·g-1·K-1 Hazards Flash point 178°C Autoignition
temperature365°C Explosive limits >0.4%  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Dibutyl sebacate (DBS) is an organic chemical, a dibutyl ester of sebacic acid. Its main use is as a plasticizer in production of plastics, namely cellulose acetate butyrate, cellulose acetate propionate, ethyl cellulose, polyvinyl butyral, polyvinyl chloride, polystyrene, and many synthetic rubbers (especially nitrile rubber and neoprene) and other plastics. It can be used for plastics in use in the food packaging industry, in plastics used for medical devices, and for pharmaceutical applications, e.g. as a plasticizer for film coating of tablets, beads, and granules.[2] It is also used as a lubricant in shaving lotions, and a flavoring additive in non-alcoholic beverages, ice cream, ices, candy, and baked goods. It provides excellent compatibility[citation needed] with a range of plastic materials, superior properties at low temperatures, and good oil resistivity. Its other names include Morflex, Kodaflex, polycizer, Proviplast 1944 and PX 404. Dibutyl sebacate is also used as a desensitizer in Otto fuel II, a torpedo monopropellant.
References
- ^ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. pp. 3–162, 15–18. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ^ chemicalland21.com Dibutyl Sebacate
This article about an organic compound is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
