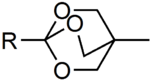- Orthoester
-
 A ball-and-stick model of ethyl orthoacetate, an orthoester.
A ball-and-stick model of ethyl orthoacetate, an orthoester.
In organic chemistry, an orthoester is a functional group containing three alkoxy groups attached to one carbon atom, i.e. with the general formula RC(OR’)3. The name can also refer to any organic compound that contains this functional group. An example of an orthoester is ethyl orthoacetate, CH3C(OCH2CH3)3, more correctly known as 1,1,1-triethoxyethane. Orthoesters are used in organic synthesis as protecting groups for esters. Orthoesters may be considered as products of exhaustive alkylation of unstable orthocarboxylic acids (the products of hydration of carboxylic acids; see also acetal).[1]
Contents
Reactions
Preparation
Orthoesters can be prepared by the reaction of nitriles with alcohols under acid catalysis:
- RCN + 3 R’OH → RC(OR’)3 + NH3
Hydrolysis
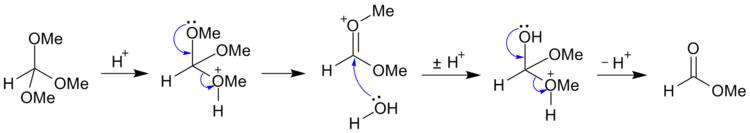
Orthoesters are readily hydrolyzed in mild aqueous acid to form esters:
- RC(OR’) 3 + H2O → RCO2R’ + 2 R’OH
For example, trimethyl orthoformate [CH(OCH3)3] may be hydrolyzed (under acidic conditions) to methyl formate and methanol;[2] and may be further hydrolyzed (under alkaline conditions) to salts of formic acid and methanol.[3]
Common Orthoesters in Practical Usage
Both trimethylorthoacetate and triethylorthoacetate are commonly used reagents in organic chemistry. Another example is the bicyclic OBO protecting group (4-methyl-2,6,7-trioxa-bicyclo[2.2.2]octan-1-yl) which is formed by the action of (3-methyloxetan-3-yl)methanol on activated carboxylic acids in the presence of Lewis acids and was developed by Elias James Corey. The group is base stable and can be cleaved in two steps under mild conditions, mildly acidic hydrolysis yields the ester of tris(hydroxymethyl)ethane which is then cleaved using e.g. an aqueous carbonate solution.[4]
References
- ^ David A. Shirley, Organic Chemistry (1968).
- ^ Clayden, Jonathan; Greeves, Nick; Warren, Stuart; Wothers, Peter (2001). Organic Chemistry (1st ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 345. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0.
- ^ United States Patent Application 20070049501, Saini; Rajesh K.; and Savery; Karen, March 1, 2007
- ^ Philip J. Kocieński "Protecting groups"; ISBN-10: 3131356030, ISBN-13: 978-3131356031
Categories:- Functional groups
- Orthoesters
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.