- Moricizine
-
Moricizine 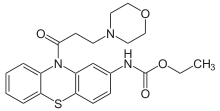
Systematic (IUPAC) name ethyl [10-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropanoyl)-10H-phenothiazin-2-yl]carbamate Clinical data Trade names Ethmozine AHFS/Drugs.com Consumer Drug Information MedlinePlus a601214 Pregnancy cat. B (U.S.) Legal status ? Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 38% Protein binding 95% Half-life 3-4 hours (healthy volunteers), 6-13 hours (cardiac disease) Identifiers CAS number 31883-05-3 
ATC code None PubChem CID 34633 DrugBank APRD01124 ChemSpider 31872 
UNII 2GT1D0TMX1 
KEGG D05077 
ChEBI CHEBI:6997 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1075 
Chemical data Formula C22H25N3O4S Mol. mass 427.518 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Moricizine (Ethmozine®) is a phenothiazine derivative with Vaughan Williams class Ic antiarrhythmic properties. It undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism, has a bioavailability of 34-38 percent, and is 95 percent bound to plasma proteins. Moricizine is extensively metabolized and may have pharmacologically active metabolites. A recent clinical study has shown that moricizine is slightly less effective than encainide or flecainide in suppressing ventricular premature depolarizations[citation needed]. Compared with disopyramide and quinidine, moricizine was equally or more effective in suppressing ventricular premature depolarizations, couplets, and nonsustained ventricular tachycardia[citation needed]. Further studies are needed comparing moricizine with other class 1 agents in the treatment of life-threatening arrhythmias; available data suggest that moricizine is comparable with these agents in the treatment of ventricular tachycardias and fibrillation. Moricizine appears to have a low incidence of serious adverse effects compared with other antiarrhythmics. This combination of apparently similar efficacy with a decreased incidence of adverse effects makes moricizine a worthwhile addition to currently available antiarrhythmic agents.
External links
Antiarrhythmic agents (C01B) Channel blockers class Ib (Phase 3←)class Ic (Phase 0→)Amiodarone • Dronedarone • Bretylium • Bunaftine • Dofetilide • Ibutilide • Nifekalant • Sotalol • Tedisamil • Vernakalant • E-4031Receptor agonists
and antagonistsIon transporters 
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
