- Masticatory muscle myositis
-
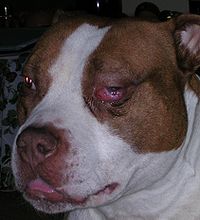 Acute MMM in an American Pit Bull Terrier
Acute MMM in an American Pit Bull Terrier
 Chronic MMM in a Rottweiler
Chronic MMM in a Rottweiler
Masticatory muscle myositis (MMM) is an inflammatory disease in dogs affecting the muscles of mastication (chewing). It is also known as atrophic myositis or eosinophilic myositis. MMM is the most common inflammatory myopathy in dogs.[1] The disease mainly affects large breed dogs.[2] German Shepherd Dogs [3] and Cavalier King Charles Spaniels may be predisposed.[4] There is a similar disease of the eye muscles found in Golden Retrievers. Symptoms of acute MMM include swelling of the jaw muscles, drooling, and pain on opening the mouth. Ophthalmic signs may include third eyelid protrusion, red eyes, and exophthalmos (protruding eyeballs).[5] In chronic MMM there is atrophy of the jaw muscles, and scarring of the masticatory muscles due to fibrosis may result in inability to open the mouth (trismus). The affected muscles include the temporalis, masseter, and pterygoid muscles. The disease is usually bilateral.
MMM is caused by the presence of 2M fibers in the muscles of the jaw. 2M fibers are not found elsewhere in the body, but they are close in structure to proteins found on the surface of bacteria. The immune system recognizes these proteins as foreign to the body and attacks them, resulting in inflammation.[2] Diagnosis of MMM is through either biopsy of the temporalis or masseter muscles or the 2M antibody assay, in which blood serum of the possible MMM-dog is reacted with temporalis tissue of a normal dog, or both. False negatives by the 2M antibody assay may be obtained if MMM is end-stage with destruction of type 2M fibers and marked fibrosis. Treatment is usually with corticosteroids such as prednisone, often with decreasing doses for up to 4–6 months, and in the case of trismus, manual opening of the mouth under anesthesia.[6] Feeding very soft or liquid food during this time is usually necessary. The ultimate degree of recovery of jaw function and muscle mass will depend upon the extent of damage to the muscle tissue. Recurrence of MMM may occur.[7] Misdiagnosis of MMM as a retroorbital abscess based on physical examination and finding of trismus leads to inappropriate treatment with antibiotics, which will not impede the progress of MMM.
References
- ^ Neumann J, Bilzer T (2006). "Evidence for MHC I-restricted CD8+ T-cell-mediated immunopathology in canine masticatory muscle myositis and polymyositis". Muscle Nerve 33 (2): 215–24. doi:10.1002/mus.20456. PMID 16270307.
- ^ a b Ettinger, Stephen J.;Feldman, Edward C. (1995). Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine (4th ed.). W.B. Saunders Company. ISBN 0-7216-6795-3.
- ^ Dewey, C.W. (2005). "Disorders of the Peripheral Nervous System" (PDF). 50° Congresso Nazionale Multisala SCIVAC. http://www.ivis.org/proceedings/scivac/2005/Dewey5_en.pdf?LA=1. Retrieved 2007-02-10.
- ^ Pitcher, GD (2007). "Atypical masticatory muscle myositis in three cavalier King Charles spaniel littermates". http://cavalierhealth.net/masticatory_muscle_myositis.htm.
- ^ Gelatt, Kirk (2002). "Treatment of Orbital Diseases in Small Animals". Proceedings of the 27th World Congress of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association. http://www.vin.com/proceedings/Proceedings.plx?CID=WSAVA2002&PID=2641. Retrieved 2007-02-10.
- ^ Chrisman, Cheryl; Clemmons, Roger; Mariani, Christopher; Platt, Simon (2003). Neurology for the Small Animal Practitioner (1st ed.). Teton New Media. ISBN 1-893441-82-2.
- ^ Clooten J, Woods J, Smith-Maxie L (2003). "Myasthenia gravis and masticatory muscle myositis in a dog". Can Vet J 44 (6): 480–3. PMC 340171. PMID 12839242. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=340171.
External links
Categories:- Dog diseases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
