- Yerkes–Dodson law
-
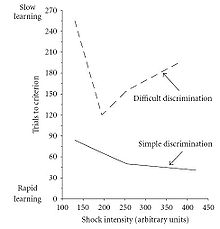
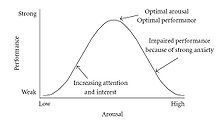
The Yerkes–Dodson law is a claimed empirical relationship between arousal and performance, originally developed by psychologists Robert M. Yerkes and John Dillingham Dodson in 1908.[1] The "law" asserts that performance increases with physiological or mental arousal, but only up to a point. When levels of arousal become too high, performance decreases. The process is often illustrated graphically as a curvilinear, inverted U-shaped curve which increases and then decreases with higher levels of arousal.
Contents
Levels of arousal
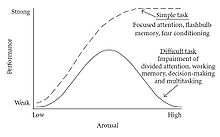
Research has found that different tasks require different levels of arousal for optimal performance. For example, difficult or intellectually demanding tasks may require a lower level of arousal (to facilitate concentration), whereas tasks demanding stamina or persistence may be performed better with higher levels of arousal (to increase motivation).
Because of task differences, the shape of the curve can be highly variable. For simple or well-learned tasks, the relationship can be considered linear with improvements in performance as arousal increases. For complex, unfamiliar, or difficult tasks, the relationship between arousal and performance becomes inverse, with declines in performance as arousal increases.
The effect of task difficulty led to the hypothesis that the Yerkes–Dodson Law can be decomposed into two distinct factors – compare bathtub curve. The upward part of the inverted U can be thought of as the energizing effect of arousal. The downward part is caused by negative effects of arousal (or stress) on cognitive processes like attention (e.g., "tunnel vision"), memory, and problem-solving.
There has been research indicating that the correlation suggested by Yerkes and Dodson exists (such as that of Broadhurst, 1959; Duffy, 1962; Anderson, 1988), but a cause of the correlation has not yet successfully been established (Anderson, Revelle, & Lynch, 1989).[2]
Relationship to glucocorticoids
A 2007 review of the effects of stress hormones (glucocorticoids) and human cognition revealed that memory performance vs. circulating levels of glucocorticoids does manifest an upside down U shaped curve and the authors noted the resemblance to the Yerkes–Dodson curve. For example, long-term potentiation (the process of forming long-term memories) is optimal when glucocorticoid levels are mildly elevated whereas significant decreases of LTP are observed after adrenalectomy (low GC state) or after exogenous glucocorticoid administration (high GC state).
This review also revealed that in order for a situation to induce a stress response, it has to be interpreted as:- novel, and/or
- unpredictable, and/or
- not controllable by the individual, and/or
- in the presence of a social evaluative threat.
It has also been shown that elevated levels of glucocorticoids enhanced memory for emotionally arousing events but lead more often than not to poor memory for material unrelated to the source of stress/emotional arousal.[3]
See also
- Drive theory
- Emotion
- Emotion and memory
- Flashbulb memory
- Humanizing Madness
- Incentive theory
- Laffer curve
References
- ^ Yerkes RM, Dodson JD (1908). "The relation of strength of stimulus to rapidity of habit-formation". Journal of Comparative Neurology and Psychology 18: 459–482.
- ^ Anderson KJ, Revelle W, Lynch MJ (1989). "Caffeine, impulsivity, and memory scanning: A comparison of two explanations for the Yerkes-Dodson Effect". Motivation and Emotion 13: 1–20.
- ^ Lupien SJ, Maheu F, Tu M, Fiocco A, Schramek TE (2007). "The effects of stress and stress hormones on human cognition: Implications for the field of brain and cognition". Brain and Cognition 65: 209–237. doi:10.1016/j.bandc.2007.02.007. PMID 17466428.
Categories:- Behavioral concepts
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.