- Methyl red
-
Methyl red 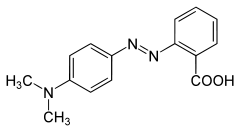
Identifiers CAS number 493-52-7  ,
,
[63451-28-5] (HCl salt),
[845-10-3] (sodium salt)KEGG C19459 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - CN(C)c2ccc(/N=N/
c1ccccc1C(O)=O)cc2
Properties Molecular formula C15H15N3O2 Molar mass 269.3 g mol−1 Density 0.791 g/cm3 Melting point 179-182 °C, 452-455 K
Hazards R-phrases R20 R21 R22 R36 R37 R38 R40  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Methyl Red (pH indicator) below pH 4.4 above pH 6.2 4.4 ↔ 6.2 Methyl red, also called C.I. Acid Red 2, is an indicator dye that turns red in acidic solutions. It is an azo dye, and is a dark red crystalline powder.
Methyl red is a pH indicator; it is red in pH under 4.4, yellow in pH over 6.2, and orange in between, with a pKa of 5.1 [1].
Murexide and methyl red are investigated as promising enhancers of sonochemical destruction of chlorinated hydrocarbon pollutants.[2]
Methyl red is classed by the IARC in group 3 - unclassified as to carcinogenic potential in humans.
Contents
Preparation
As an azo dye, Methyl Red may be prepared by diazotization of anthranilic acid, followed by reaction with dimethylaniline:[3]
Methyl red test
In microbiology, methyl red is used in the Methyl Red (MR) Test, used to identify bacteria producing stable acids by mechanisms of mixed acid fermentation of glucose (cf. Voges–Proskauer (VP) test).
The methyl red test is the "M" portion of the four IMViC tests used to characterize enteric bacteria. The methyl red test is used to identify enteric bacteria based on their pattern of glucose metabolism. All enterics initially produce pyruvic acid from glucose metabolism. Some enteric subsequently use the mixed acid pathway to metabolize pyruvic acid to other acids, such as lactic, acetic, and formic acids. These bacteria are called methyl-red positive and include Escherichia coli and Proteus vulgaris. Other enterics subsequently use the buytylene glycol pathway to metabolize pyruvic acid to neutral end-products. These bacteria are called methyl-red-negative and include Serratia marcescens and Enterobacter aerogenes.[2]
Process
An isolate is inoculated into a tube with a sterile transfer loop. The tube is incubated at 35°C for 2-5 days. After incubation, 2.5ml of the medium is transferred to another tube. Five drops of the pH indicator methyl red is added to this tube. The tube is gently rolled between the palms of the hands to disperse the methyl red.[2]
Expected results
Enterics that subsequently metabolize pyruvic acid to other acids lower the pH of the medium to 4.2. At this pH, methyl red turns red. A red color represents a positive test. Enterics that subsequently metabolize pyruvic acid to neutral end-products lower the pH of the medium to only 6.0. At this pH, methyl red is yellow. A yellow color represents a negative test.[2]
See also
References
- ^ IB chemistry Higher Level: http://ibchem.com/IB/ibnotes/full/aab_htm/18.6.htm
- ^ a b c d [1][dead link]
- ^ H. T. Clarke and W. R. Kirner (1941), "Methyl Red", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv1p0374; Coll. Vol. 1: 374
- "Microbiology, A Photographic Atlas for the Laboratory", Alexander, Street, Pearson Education, 2001.
External links
- Nile Chemicals -- Methyl Red A site showing some extra information on methyl red.
- Synthesis of methyl red
Categories:- PH indicators
- IARC Group 3 carcinogens
- Azo dyes
- Anthranilic acids
- CN(C)c2ccc(/N=N/
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

