- Plutonium(IV) oxide
-
Plutonium(IV) oxide 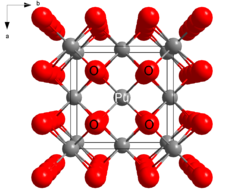 Plutonium(IV) oxideSystematic namePlutonium(4+) oxideOther namesPlutonium dioxide
Plutonium(IV) oxideSystematic namePlutonium(4+) oxideOther namesPlutonium dioxideIdentifiers CAS number 12059-95-9 
ChemSpider 10617028 
Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [O--].[O--].[Pu+4]
Properties Molecular formula O2Pu Molar mass 276.06 g mol−1 Exact mass 275.990 g mol-1 Appearance Dark yellow crystals Density 11.5 g cm-3 Melting point 2400 °C, 2673 K, 4352 °F
Boiling point 2800 °C, 3073 K, 5072 °F
Structure Crystal structure Fluorite (cubic), cF12 Space group Fm3m, No. 225 Coordination
geometryTetrahedral (O2–); cubic (PuIV) Hazards Main hazards RADIOACTIVE  (verify) (what is:
(verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Plutonium(IV) oxide is the chemical compound with the formula PuO2. This high melting point solid is a principal compound of plutonium. It can vary in color from yellow to olive green, depending on the particle size, temperature and method of production.[1]
Contents
Structure
PuO2 crystallizes in the fluorite motif, with the Pu4+ centers organized in a face-centered cubic array and oxide ions occupying tetrahedral holes.[2] PuO2 owes utility as a nuclear fuel to the fact that vacancies in the octahedral holes allows room for fissile products. In nuclear fission, one atom of plutonium splits into two. The vacancy of the octahedral holes provides room for the new product and allows the PuO2 monolith to retain its structural integrity.
Synthesis
Plutonium metal spontaneously oxidizes to PuO2 in an atmosphere of oxygen. Plutonium dioxide is mainly produced by calcination of plutonium(IV) oxalate, Pu(C2O4)2·6H2O, at 300 °C. Plutonium oxalate is obtained during the reprocessing of nuclear fuel.
Applications
PuO2 is used in MOX fuels for nuclear reactors. Plutonium-238 dioxide is used as fuel for several deep-space spacecraft such as the 'New Horizons' Pluto probe. The isotope decays by emitting α-particles which then generate heat (see radioisotope thermoelectric generator). There have been concerns that an accidental orbital earth re-entry might lead to the break-up and/or burn-up of a spacecraft, resulting in the dispersal of the plutonium, either over a large tract of the planetary surface or within the upper atmosphere.
Physicist Peter Zimmerman, following up a suggestion by Ted Taylor, demonstrated that a low-yield (1-kiloton) nuclear bomb could be made relatively easily from plutonium oxide.[3]
Toxicology
-
- See also, Plutonium Toxicity
Plutonium oxide is highly toxic to humans, especially via inhalation.[4] As with all plutonium compounds, it is subject to control under the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. Due to the radioactive alpha decay of plutonium, all of its compounds, PuO2 included, as well as plutonium metal, are warm to the touch.
See also
References
- ^ "Nitric acid processing". Los Alamos Laboratory. http://arq.lanl.gov/source/orgs/nmt/nmtdo/AQarchive/3rdQuarter08/page3.shtml.
- ^ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, A. (1984). Chemistry of the Elements. Oxford: Pergamon. p. 1471. ISBN 0-08-022057-6.
- ^ Michael Singer, David Weir, and Barbara Newman Canfield (Nov. 26, 1979). "Nuclear Nightmare: America's Worst Fear Come True". New York Magazine.
- ^ "Toxicological Profile For Plutonium". U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. 2007-09-27. http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp143.pdf. Retrieved 2009-04-23.
External links
Plutonium compounds Categories:- Plutonium compounds
- Oxides
- Nuclear materials
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

