- Patriarchate of Aquileia (state)
-
For other uses, see Patriarchate of Aquileia.
Patriarchate of Aquileia
Patriarchae Aquileiensis
Patria del FriuliState of the Holy Roman Empire ← 
1077–1445  →
→
 →
→

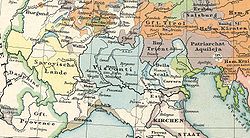
Flag Coat of arms Imperial Kingdom of Italy in the mid 14th century;
Patriarchate of Aquileia shown centre right in maroonCapital Aquileia
Udine (from 1238)Language(s) Latin, Friulian Religion Roman Catholic Government Prince-Bishopric Historical era Middle Ages - Imperial immediacy
granted by Henry IV
1077- County of Görz
emerged1127 - Terraferma annexed
by Venice
1420- Incorporated by Venice 1445 - Dissolved by Benedict XIV 1751 The Patriarchate of Aquileia (Italian: Patria del Friuli, Friulian: Patrie dal Friûl) was an Imperial State in the Friulian region of Northeastern Italy under the control of the Patriarchs of Aquileia.
Contents
Foundation
During the Investiture Controversy in 1077, King Henry IV of Germany on his way back from Canossa vested Patriarch Sieghard of Beilstein with immediate comital rights in the eastern Friulian lands of the March of Verona. The former Veronese margrave, the Zähringen Duke Berthold II of Carinthia, had been deposed as he had sided with antiking Rudolf of Rheinfelden, and his successor Liutold of Eppenstein only retained a smaller margraviate.
Sieghard in turn safely conducted the king across the Alps. Back in Germany, King Henry in addition nominally assigned the suzerainty over the marches of Carniola and Istria to the patriarchs as ecclesiastical Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. The act, traditionally regarded as the birth of the ecclesiastical state of Aquileia, led to a long-time conflict with the rivaling margraves from the Carinthian House of Sponheim and the Andechs dukes of Merania.
Expansion
The Patriarchate subsequently extended its political control in the area: regions under Aquileian control in the following centuries included the Friulian lands up to Cadore, the city of Trieste and the central parts of the Istrian peninsula. At its maximum height, the Patriarchate of Aquileia was one of the largest states in Italy. Noblemen from the Patriarchate were protagonists in the Crusades. In 1186 Patriarch Gottfried (Gitifredo Tedesco) crowned Frederick Barbarossa's son, Henry VI, as King of Italy: in retaliation, Pope Urban III deposed him.
From 1127 the vogts at Gorizia from the Meinhardiner dynasty emerged from Aquileia, calling themselves Counts of Görz. Their autonomy was strengthened, when they inherited the Imperial County of Tyrol in 1253 and were elevated to Princes of the Holy Roman Empire by Emperor Charles IV in 1365.
In the early 13th century, particularly under Volchero (1204–1218) and Bertrand (1218–1251), the Patriarchate had a flourishing economy and cultural life, favoured by good roads network. Damaged by earthquakes and other calamities, and reduced to a few hundred inhabitants, Aquileia was nearly abandoned in the 14th century. The capital of the state was moved first to Cividale and then, from 1238, to Udine in central Friuli, which had been a favourite residence of the patriarch since the 13th century and soon became a large city.
Rivalry with Venice
The patriarchs had regained the rule of the Istrian march from the Dukes of Merania in 1209. However, they had to cope with the rising naval power of the Republic of Venice, which in the late 13th century had occupied the western Istrian coast from Capodistra (Koper) down to Rovinj (Rovigno). In 1291 a peace was made in Treviso, whereupon the western coast of the peninsula fell to La Serenissima. In the late century the patriarchate had to face the increasing rivalry with Venice, as well as the inner strifes between its vassals, and also became encroached in the endless wars between Guelphs and Ghibellines. In 1331 Venice also incorporated Pola (Pula) in the south. A certain recovery occurred during the rule of Bertrand (1334–1350), a successful administrator and military leader. He was killed in 1350 in a plot, at the age of ninety.
The Counts of Görz had retained some interior Istrian lands around Pazin (Mitterburg), which they bequested to the Austrian House of Habsburg in 1374. In view of the Venice threat, the city of Trieste submitted to the Habsburgs in 1382.
Since the transfer of the patriarchal residence to Udine, the Venetians had never lived in peace with the Patriarchate, of whose Imperial favour and tendencies they were jealous. From about 1400, La Serenissima under Doge Michele Steno and his successor Tommaso Mocenigo began to enlarge its dogado by occupying the Aquileia hinterlands. At the same time, thePatriarchate suffered a series of inner strifes between the citizens of Cividale and Udine.
In 1411 this turned into a war which was to mark the end of the Patriarchate, Cividale having received support from most of the Friulian communes, the Carraresi of Padua, King Sigismund of Germany, also King of Hungary, while Udine was backed by the Venetians. In the December of that year an Imperial army captured Udine and, in the following January, Louis of Teck was implemented as patriarch in the city's cathedral. On July 23, 1419 the Venetians conquered Cividale and prepared to do the same with Udine. The city fell on June 7, 1420 after a longe siege. Soon afterwards Gemona, San Daniele, Venzone and Tolmezzo followed.
Secularisation
The temporal authority of the patriarch was lost in 7 July 1420 when its territories were secularised by Venice. Doge Francesco Foscari in 1433 signed an agreement with Emperor Sigismund, whereby the Empire ceded the Domini di Terraferma, stretching from the Adriatic Sea to the Alps, to the Republic, then officially as an Imperial fief. The territory around Gorizia and Aquileia proper was retained by the Counts of Görz; the last Count Leonhard in 1500 bequested his lands to Archduke Maximilian I of Austria, who also annexed the city of Gradisca in 1511. The former Görz territory were incorporated into the Inner Austrian possessions of the Habsburgs.
In 1445, after Patriarch Ludovico Trevisan at the Council of Florence had acquiesced in the loss of his ancient temporal estate in return for an annual salary of 5,000 ducats allowed him from the Venetian treasury. Henceforth only Venetians were allowed to hold the title of Patriarch of Aquileia. The former Friulian state was incorporated in the Venetian Republic with the name of Patria del Friuli, ruled by a General Proveditor or a Luogotenente living in Udine. In 1523 Emperor Charles V ultimately renounced any Imperial feudal rights to the former Aquileia territory.
References
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Shahan, Thomas J. (1913). "Aquileia". In Herbermann, Charles. Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company.Categories:
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Shahan, Thomas J. (1913). "Aquileia". In Herbermann, Charles. Catholic Encyclopedia. Robert Appleton Company.Categories:- Former countries in Europe
- States of the Holy Roman Empire
- States and territories established in 1077
- States and territories disestablished in 1445
- Prince-Bishops of the Holy Roman Empire
- Veneto
- Patriarch of Aquileia
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.